m (Reverted edits by Windows NT 6.0) Tag: Visual edit |
(Undo revision 20828 by TheCharizard31 (talk)) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|source model = |
|source model = |
||
|released = November 20, 1985 |
|released = November 20, 1985 |
||
| + | as [[Windows 1.0]] |
||
|discontinued = |
|discontinued = |
||
| − | |latest release version = [[Windows 10]] Version |
+ | |latest release version = [[Windows 10]] Version 1809 (v10.0.17763) |
| − | |latest preview version = |
+ | |latest preview version = [[Windows 10]] Version 20H1 (v10.0.18362.53) |
|marketing target = Personal computing |
|marketing target = Personal computing |
||
|programmed in = C, C++, Assembly |
|programmed in = C, C++, Assembly |
||
|language = 137 languages |
|language = 137 languages |
||
| − | |update model = [[Windows Update]]<br />[[Windows Anytime Upgrade]]<br />[[Windows Store]]<br />Windows Server Update Services |
+ | |update model = [[Windows Update]]<br />[[Windows Anytime Upgrade]]<br />[[Windows Store]]<br />[[Windows Server Update Services]] |
|package manager = [[Windows Installer]] (.msi)<br />[[Windows Store]] (.appx |
|package manager = [[Windows Installer]] (.msi)<br />[[Windows Store]] (.appx |
||
|supported platforms = ARM, [[IA-32]], Itanium, [[x86-64]], DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC |
|supported platforms = ARM, [[IA-32]], Itanium, [[x86-64]], DEC Alpha, MIPS, PowerPC |
||
| Line 20: | Line 21: | ||
|influenced by = |
|influenced by = |
||
|ui = [[Windows Shell]] |
|ui = [[Windows Shell]] |
||
| − | |license = Proprietary commercial software |
+ | |license = [[Proprietary commercial software]] |
|rtm date = |
|rtm date = |
||
|ga date = |
|ga date = |
||
| − | |kernel type = [[Windows NT]] family: [[Hybrid kernel|Hybrid]]<br />[[Windows 9x]] and earlier: [[ |
+ | |kernel type = [[Windows NT]] family: [[Hybrid kernel|Hybrid]]<br />[[Windows 9x]] and earlier: [[Microsoft DOS]] |
|prev = |
|prev = |
||
|next = |
|next = |
||
|website = {{URL|http://windows.microsoft.com/}} |
|website = {{URL|http://windows.microsoft.com/}} |
||
| − | |support status = |
+ | |support status =Supported |
|logo = Windows logo Cyan rgb D.png}} |
|logo = Windows logo Cyan rgb D.png}} |
||
'''Microsoft Windows''' is a group of several [[Graphical user interface|graphical]] [[operating system]] families, all of which are developed, marketed, and sold by [[Microsoft]]. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Windows families include [[Windows NT]] and [[Windows Embedded]]; these may encompass subfamilies, e.g. [[Windows Embedded Compact]] (Windows CE) or [[Windows Server]]. Defunct Windows families include [[Windows 9x]], [[Windows Mobile]] and [[Windows Phone]]. |
'''Microsoft Windows''' is a group of several [[Graphical user interface|graphical]] [[operating system]] families, all of which are developed, marketed, and sold by [[Microsoft]]. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Windows families include [[Windows NT]] and [[Windows Embedded]]; these may encompass subfamilies, e.g. [[Windows Embedded Compact]] (Windows CE) or [[Windows Server]]. Defunct Windows families include [[Windows 9x]], [[Windows Mobile]] and [[Windows Phone]]. |
||
| Line 44: | Line 45: | ||
*[[Windows 1.0]] |
*[[Windows 1.0]] |
||
*[[Windows 2.0]] |
*[[Windows 2.0]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows 2.1x]] |
||
*[[Windows 3.0]] |
*[[Windows 3.0]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows 3.1x]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows NT 3.1]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows 3.5]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows 3.51]] |
||
*[[Windows 95]] |
*[[Windows 95]] |
||
| − | *[[Windows |
+ | *[[Windows 96]] |
| + | *[[Windows NT 4.0]] |
||
*[[Windows 98]] |
*[[Windows 98]] |
||
| − | *[[Windows |
+ | *[[Windows NT 5.0]] |
*[[Windows 2000]] |
*[[Windows 2000]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Server 2000]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Me]] |
||
*[[Windows XP]] |
*[[Windows XP]] |
||
| − | *[[Windows |
+ | *[[Windows Server 2003]] |
| + | *[[Windows Server 2003 R2]] |
||
*[[Windows Vista]] |
*[[Windows Vista]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Home Server]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Server 2008]] |
||
*[[Windows 7]] |
*[[Windows 7]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Server 2008 R2]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows 7.1]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Server 2008 R3]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Home Server 2011]] |
||
*[[Windows 8]] |
*[[Windows 8]] |
||
*[[Windows RT]] |
*[[Windows RT]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Server 2012]] |
||
*[[Windows 8.1]] |
*[[Windows 8.1]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Server 2012 R2]] |
||
*[[Windows 10]] |
*[[Windows 10]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Server 2016]] |
||
| + | *[[Windows Server 2019]] |
||
==History== |
==History== |
||
| Line 191: | Line 211: | ||
| − | ====2006-2012 as [[Windows Vista]]-[[Windows 7|7]]==== |
+ | ====2006-2012 as [[Windows Vista]]-[[Windows 7.1|7.1]]==== |
[[File:Windows_logo_-_2006.svg.png]] |
[[File:Windows_logo_-_2006.svg.png]] |
||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
====2012-2015 as [[Windows 8]]==== |
====2012-2015 as [[Windows 8]]==== |
||
Revision as of 09:20, 30 April 2019
Microsoft Windows is a group of several graphical operating system families, all of which are developed, marketed, and sold by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. Active Windows families include Windows NT and Windows Embedded; these may encompass subfamilies, e.g. Windows Embedded Compact (Windows CE) or Windows Server. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile and Windows Phone.
Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs).[1] Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal computer (PC) market with over 90% market share, overtaking Mac OS, which had been introduced in 1984. Apple came to see Windows as an unfair encroachment on their innovation in GUI development as implemented on products such as the Lisa and Macintosh (eventually settled in court in Microsoft's favor in 1993). On PCs, Windows is still the most popular operating system. However, in 2014, Microsoft admitted losing the majority of the overall operating system market to Android,[2] because of the massive growth in sales of Android smartphones. In 2014, the number of Windows devices sold was less than 25% that of Android devices sold. This comparison however may not be fully relevant, as the two operating systems traditionally target different platforms. Still, numbers for server use of Windows (that are comparable to competitors) show one third market share, similar to for end user use.
As of December 2017[update], the most recent version of Windows for PCs, tablets, smartphones and embedded devices is Windows 10. The most recent versions for server computers is Windows Server 2016. A specialized version of Windows runs on the Xbox One video game console.[3]
Versions
- See also: List of Microsoft Windows versions
There have been many versions of Windows since its introduction in 1985, ranging from 16-bit to 64-bit, for both client and server applications.
All Versions
- Windows 1.0
- Windows 2.0
- Windows 2.1x
- Windows 3.0
- Windows 3.1x
- Windows NT 3.1
- Windows 3.5
- Windows 3.51
- Windows 95
- Windows 96
- Windows NT 4.0
- Windows 98
- Windows NT 5.0
- Windows 2000
- Windows Server 2000
- Windows Me
- Windows XP
- Windows Server 2003
- Windows Server 2003 R2
- Windows Vista
- Windows Home Server
- Windows Server 2008
- Windows 7
- Windows Server 2008 R2
- Windows 7.1
- Windows Server 2008 R3
- Windows Home Server 2011
- Windows 8
- Windows RT
- Windows Server 2012
- Windows 8.1
- Windows Server 2012 R2
- Windows 10
- Windows Server 2016
- Windows Server 2019
History
- Main article: History of Microsoft Windows
Windows was first originated as an add-on to MS-DOS to provide a graphical user interface to the traditional command-line system.
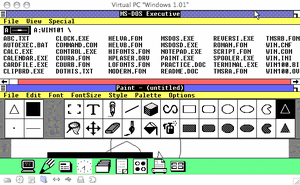
A typical Windows 1.0 desktop.
The first independent version of Microsoft Windows, version 1.0, released in November 1985, lacked a degree of functionality and achieved little popularity. Windows 2.0 was released in November 1987 and was slightly more popular than its predecessor. Windows 2.03 (release date January 1988) had introduced overlapping windows, which led to Apple Computer filing a suit against Microsoft alleging copyright infringement.
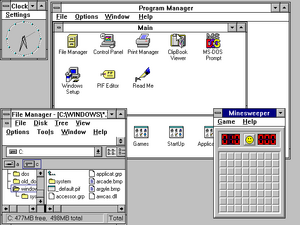
A typical Windows 3.11 Workgroup desktop.
Windows 3.0, released in 1990, was the first Windows version to achieve broad commercial success, selling 2 million copies in the first six months. It featured improvements to the user interface and to multitasking capabilities.
In July 1993, Microsoft released Windows NT based on IBM OS/2 technology (which Microsoft had been co-developing for several years prior). NT was targeted at businesses rather than home users, although these separate lines would later be combined.
In August 1995, Microsoft released Windows 95, which introduced the Start Menu which is still in use 15 years later. The next in line was Microsoft Windows 98 released in June, 1998. Substantially criticized for its slowness compared with Windows 95, many of its basic problems were later rectified with the release of Windows 98 Second Edition in 1999.
As part of its business line, Microsoft released Windows 2000 in February 2000, which was used for servers and workstations alike. The consumer version was Windows Me (Millennium Edition), released in September 2000. Windows Me attempted to implement a number of new technologies for Microsoft, most notably Universal Plug and Play, however the OS was substantially criticized for its lack of compatibility and stability.
In October 2001, Microsoft released Windows XP, a version built on the Windows NT kernel that also retained the consumer-oriented usability of Windows 95 and its successors. It shipped in two distinct editions, "Home" and "Professional", the former lacking many of the superior security and networking features of the Professional edition. Additionally, the "Media Center" edition was released in 2003, with an emphasis on support for DVD and TV functionality including program recording and a remote control.
Windows Server 2003 was introduced in April 2003, replacing the Windows 2000 line of server products with a number of new features and a strong focus on security; this was followed in December 2005 by Windows Server 2003 R2 (Release 2).
The long-awaited Windows Vista, codenamed Longhorn, was released in 2007 with 5 editions. Vista was built on the more recent and more stable platform of Server 2003. Windows Server 2008 was introduced in February 2008.
In October 2009, Windows 7 was launched as the successor to Vista, and is considered to be a lot more stable and usable than its predecessor. At the same time, Windows Server 2008 R2 was launched as an update to the server line.
Windows 8
- Main article: Windows 8
A roadmap timeline slide shown by Microsoft at the 2009 Professional Developers Conference shows that Code Name "Windows 8" is scheduled to be released sometime around 2012.
Andrew Glass of Microsoft has confirmed Windows 8 will support Unicode 5.2.
Development and other aspects of Windows 8 have not been detailed in public, although job listings have mentioned improved functionality for file access in branch offices.
Interface
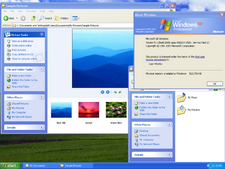
A typical Windows XP desktop.
The most obvious feature of Windows is a window, or a container for other graphical objects. A Window in Microsoft Windows typically contains a status bar, title bar, minimize and maximize buttons, close button, and system menu (also called the windows menu or control menu). Another prominent feature since Windows 95 and NT 4.0 is the desktop, which holds various icons that the user can double-click to open. The Start Button and Start Menu, attached to the taskbar and typically below the desktop, gives users access to installed programs and many of the other features of the operating system.
Due to these and features, Windows makes it possible to perform most common tasks, some quite complex, with very little computer knowledge. Windows also comes with features to help the disabled through its accessibility options. Under Windows XP, these features include the Narrator, Magnifier and contrast display mode.
Logo Timeline
1985-2001 as Microsoft Windows 1.0x-2.x

This logo is still on VMWare Player.
1988-2001 as Microsoft Windows 3.0

still on VMWare Player.
1991-2010 as Microsoft Windows 3.1-2000

This favicon logo is still on YouTube.
1995-Present
1995-2006 as Microsoft Windows 9x

This logo is still on Amazon.com.
2001-2014 as Windows XP

This favicon logo is still in other stores in other locations.
2006-2012 as Windows Vista-7.1
2012-2015 as Windows 8

This logo is in some other stores.
2015-Present as Windows 10

This logo is still used today!
Widespread Usage
Microsoft Windows is installed on the vast majority of personal computers. A July 2005 poll of Network Computing magazine readers found that 90% of their organizations used Microsoft's desktop operating systems . It has achieved enormous market penetration due to the domination of MS-DOS in the early days of PC compatible computers (IBM PC clones). It is also the primary platform for Microsoft Office and most non-console computer games.
The widespread use of Microsoft's operating system has benefited from not being tied to the success of one hardware manufacturer and from Microsoft's willingness to license the operating system to manufacturers. This is in contrast with Apple Computer, which does not license Mac OS X to other manufacturers, and Sun Microsystems, which did not license Solaris before it was made free and open-source. However, the wide spectrum of possible hardware permutations with Microsoft Windows is also a major source of computer problems because of hardware-software incompatibilities for consumers.
In the past, companies who wanted to be in the computer business had to create their own operating systems (such as the Amiga, BBC Micro or ZX Spectrum) or choose another OS; even an exclusive license with one vendor was significantly cheaper than developing and supporting a new operating system and software base.
Due to Microsoft's extensive licensing agreements with many computer vendors, Windows presently comes pre-installed on most computers as a bundled OEM version, making it the default or only choice for most of the market.
For some consumers, Windows is the only valid option for a computing environment, or it is mandated by their workplace; additionally, an unfamiliarity with other operating systems results in a lack of desire to switch to other operating systems. A significant percentage of computer users simply lack the technical knowledge needed to install an operating system.
Finally, the large base of software available exclusively for the Windows family of operating systems has become the single largest self-perpetuating reason for the popularity of Windows. In recent years, many companies have been started with the sole intention of releasing Windows software; the fact that there is already a large customer base in place is reason enough for such companies to spend their resources solely on Windows software development. As a result, the fact that many companies are supporting Windows exclusively is a self-reinforcing reason for customers to choose Windows.
Maintaining compatibility in a new release of Windows with this large collection of software designed to run on older flavors of Windows consumes a large part of the resources of the Windows development team.
Security
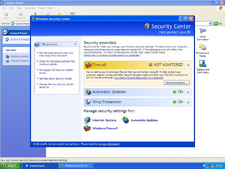
The Windows XP Security Center supplied in Service Pack 2.
Security has been a major weakness of Windows for many years, and even Microsoft itself has been the victim of cracks and hacks . Due to the widespread usage of Windows on personal computers, many crackers (also known as black hat hackers) have targeted Windows rather than the lesser used operating systems such as Linux, Unix, Mac OS X, and FreeBSD. Some believe that due being designed for security in a multi-user and/or networked environment some other operating systems have a relatively small number of security issues. Windows was originally designed for ease-of-use on a single-user PC without a network connection, and did not have security features built in from the outset. Combined with occasionally flawed code (such as buffer overflows), Windows is a continuous target of worms and virus writers. Furthermore, until Service Pack 2 of Windows XP most versions of Windows were shipped with important security features disabled by default, and vulnerable albeit useful system services enabled by default. In June 2005, Bruce Schneier's Counterpane Internet Security reported that it had seen over 1,000 new viruses and worms in the previous six months.
Microsoft publicly admitted their ongoing security problems shortly after the turn of the century and now claims to regard security as their number one priority. As a result, Service Pack 2 for Windows XP greatly increased the security of the operating system. Microsoft releases security patches through its Windows Update service approximately once a month (usually the second Tuesday of the month), although critical updates are made available at shorter intervals when necessary. In Windows 2000 (Service Pack 3 and later), Windows Me, and Windows XP, updates can be automatically downloaded and installed if the user selects to do so.
As another step in their focus on security, Microsoft has released Windows Defender (formerly Windows AntiSpyware and Giant AntiSpyware) a free program designed to protect against spyware and other unwanted software.
A study conducted by Kevin Mitnick and marketing communications firm Avantgarde found that an unprotected and unpatched Windows XP system lasted only 4 minutes on the Internet before it was compromised . The AOL/National Cyber Security Alliance Online Safety Study of October 2004 determined that 80% of Windows users were infected by at least one spyware/adware product . Much documentation is available describing how to increase the security of Microsoft Windows products. Typical suggestions include deploying Microsoft Windows behind a hardware or software firewall, running anti-virus and anti-spyware software, and installing patches as they become available through Windows Update.
See also
- General
- Further reading
References
- ↑ "The Unusual History of Microsoft Windows". Retrieved April 22, 2007.
- ↑ Keizer, Gregg (July 14, 2014). "Microsoft gets real, admits its device share is just 14%". IDG. Archived from the original on August 21, 2016. "[Microsoft's chief operating officer] Turner's 14% came from a new forecast released last week by Gartner, which estimated Windows' share of the shipped device market last year was 14%, and would decrease slightly to 13.7% in 2014. [..] Android will dominate, Gartner said, with a 48% share this year"
- ↑ "Xbox One Architecture Finally Explained - Runs OS 'Virtually Indistinguishable' from Windows 8". WCCFtech. Archived from the original on September 6, 2015.
External links
Official
- Microsoft's Official Windows Website
- Official Promotional Website (Windows.com)
- Windows history time line from Microsoft
Tips and documentation
- How to run multiple versions of Windows on one PC
- Tech-Recipes Windows Guide – listing of almost 500 Windows Tutorials
- The Windows Documentation Project (wiki)
- Securing Microsoft Windows (for Home and Small Business Users)
- Symantec Anti-Virus Research Center – excellent informational security resource, and Symantec are makers of Norton Anti-Virus (third party software sold separately).
- dotwhat? - File Extension Listing – a huge listing of file extensions and the programs that use them
- Windows – tips and tricks for Windows 98, ME, NT, 2000 and XP
- Windows Support Script
- The Windows Wiki
- Vernalex's Windows Services Utility – an unofficial list of most Windows services with detailed descriptions and recommended run states
Programming Microsoft Windows
Libraries
- RSWL – free Reliable Software C++ Windows API library.
Reviews and evaluation
- Paul Thurrott's SuperSite for Windows – an exhaustive evaluation of Microsoft's products and technologies
- "Time to Live on the Network" – a security study by Kevin Mitnick and AvantGarde (PDF)
- Windows XP: rough around the edges – an UI review of Windows XP
- Frank Mahler's Interface Hall Of Shame (in German)
- AOL/National Cyber Security Alliance Online Safety Study (October 2004) (PDF)
- Interface Hall of Shame – an analysis of user interfaces with a focus on Windows
Other
- Windows history – a Windows history time line graph by Éric Lévénez (detailed, continually updated)
- GUIdebook: Windows Gallery – a website dedicated to preserving and showcasing graphical user interfaces
- Windows 20th Birthday
Microsoft Windows family
|
|---|
| Versions • Components • History |
| Original |
| DOS-based |
| Windows 1.0 • Windows 2.0 • Windows 2.1 (Windows/286 • Windows/386) • Windows 3.0 • Windows 3.1 |
| Windows 9x |
| Windows 95 • Windows 98 • Windows Me |
| Windows NT |
| Early versions |
| Windows NT 3.1 • Windows NT 3.5 • Windows NT 3.51 • Windows NT 4.0 • Windows 2000 |
| Client |
| Windows XP (development) • Windows Vista (editions • development) • Windows 7 (editions • development) • Windows 8 • Windows 10 • Windows 11 |
| Windows Server |
| Server 2003 • Server 2008 (2008 R2) • HPC Server 2008 • Home Server • Small Business Server • Essential Business Server • Windows Server 2012 • Windows Server 2016 • Windows Server 2019 • Windows Server 2022 |
| Specialized |
| Windows Embedded • Windows PE • Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PCs |
| Mobile |
| Windows Mobile • Windows Phone |
| Cancelled |
| Cairo • Nashville • Neptune • Odyssey • Windows 10X |
| Related |
| Metro • Midori • OS/2 • Windows Aero • Windows Setup • Windows XP themes • Microsoft Plus! |

